The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican (Italian: Basilica Papale di San Pietro in Vaticano), or simply Saint Peter's Basilica (Latin: Basilica Sancti Petri), is a church of the Italian High Renaissance located in Vatican City, an independent microstate enclaved within the city of Rome, Italy. It was initially planned in the 15th century by Pope Nicholas V and then Pope Julius II to replace the aging Old St. Peter's Basilica, which was built in the fourth century by Roman emperor Constantine the Great. Construction of the present basilica began on 18 April 1506 and was completed on 18 November 1626.
Designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, and Carlo Maderno, with piazza and fittings by Gian Lorenzo Bernini, St. Peter's is one of the most renowned works of Italian Renaissance architecture and is the largest church in the world by interior measure. While it is neither the mothe...Read more
The Papal Basilica of Saint Peter in the Vatican (Italian: Basilica Papale di San Pietro in Vaticano), or simply Saint Peter's Basilica (Latin: Basilica Sancti Petri), is a church of the Italian High Renaissance located in Vatican City, an independent microstate enclaved within the city of Rome, Italy. It was initially planned in the 15th century by Pope Nicholas V and then Pope Julius II to replace the aging Old St. Peter's Basilica, which was built in the fourth century by Roman emperor Constantine the Great. Construction of the present basilica began on 18 April 1506 and was completed on 18 November 1626.
Designed principally by Donato Bramante, Michelangelo, and Carlo Maderno, with piazza and fittings by Gian Lorenzo Bernini, St. Peter's is one of the most renowned works of Italian Renaissance architecture and is the largest church in the world by interior measure. While it is neither the mother church of the Catholic Church nor the cathedral of the Diocese of Rome (these equivalent titles being held by the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran in Rome), St. Peter's is regarded as one of the holiest Catholic shrines. It has been described as "holding a unique position in the Christian world", and as "the greatest of all churches of Christendom."
Catholic tradition holds that the basilica is the burial site of Saint Peter, chief among Jesus's apostles and also the first Bishop of Rome (Pope). Saint Peter's tomb is directly below the high altar of the basilica, also known as the Altar of the Confession. For this reason, many popes, cardinals and bishops have been interred at St. Peter's since the Early Christian period.
St. Peter's is famous as a place of pilgrimage and for its liturgical functions. The pope presides at a number of liturgies throughout the year both within the basilica or the adjoining St. Peter's Square; these liturgies draw audiences numbering from 15,000 to over 80,000 people. St. Peter's has many historical associations, with the early Christian Church, the Papacy, the Protestant Reformation and Catholic Counter-Reformation and numerous artists, especially Michelangelo. As a work of architecture, it is regarded as the greatest building of its age. St. Peter's is one of the four churches in the world that hold the rank of Major papal basilica, all four of which are in Rome, and is also one of the Seven Pilgrim Churches of Rome. Contrary to popular misconception, it is not a cathedral because it is not the seat of a bishop; the cathedra of the pope as bishop of Rome is at the Archbasilica of Saint John Lateran.
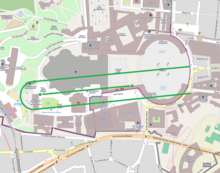 A modern conjectural reconstruction of the relative locations of the circus, and the medieval and current Basilicas of St. Peter[1]
A modern conjectural reconstruction of the relative locations of the circus, and the medieval and current Basilicas of St. Peter[1]After the crucifixion of Jesus, it is recorded in the Biblical book of the Acts of the Apostles that one of his twelve disciples, Simon known as Saint Peter, a fisherman from Galilee, took a leadership position among Jesus' followers and was of great importance in the founding of the Christian Church. The name Peter is "Petrus" in Latin and "Petros" in Greek, deriving from petra which means "stone" or "rock" in Greek, and is the literal translation of the Aramaic "Kepa", the name given to Simon by Jesus. (John 1:42, and see Matthew 16:18)
Catholic tradition holds that Peter, after a ministry of thirty-four years, travelled to Rome and met his martyrdom there along with Paul on 13 October 64 AD during the reign of the Roman Emperor Nero. His execution was one of the many martyrdoms of Christians following the Great Fire of Rome. According to Jerome, Peter was crucified head downwards, by his own request because he considered himself unworthy to die in the same manner as Jesus.[2] The crucifixion took place near an ancient Egyptian obelisk in the Circus of Nero.[3] The obelisk now stands in St. Peter's Square and is revered as a "witness" to Peter's death. It is one of several ancient Obelisks of Rome.[4]
According to tradition, Peter's remains were buried just outside the Circus, on the Mons Vaticanus across the Via Cornelia from the Circus, less than 150 metres (490 ft) from his place of death. The Via Cornelia was a road which ran east-to-west along the north wall of the Circus on land now covered by the southern portions of the Basilica and St. Peter's Square. A shrine was built on this site some years later. Almost three hundred years later, Old St. Peter's Basilica was constructed over this site.[3]
The area now covered by the Vatican City had been a cemetery for some years before the Circus of Nero was built. It was a burial ground for the numerous executions in the Circus and contained many Christian burials because for many years after the burial of Saint Peter many Christians chose to be buried near Peter.[citation needed]
In 1939, in the reign of Pope Pius XII, 10 years of archaeological research began under the crypt of the basilica in an area inaccessible since the ninth century. The excavations revealed the remains of shrines of different periods at different levels, from Clement VIII (1594) to Callixtus II (1123) and Gregory I (590–604), built over an aedicula containing fragments of bones that were folded in a tissue with gold decorations, tinted with the precious murex purple. Although it could not be determined with certainty that the bones were those of Peter, the rare vestments suggested a burial of great importance. On 23 December 1950, in his pre-Christmas radio broadcast to the world, Pope Pius XII announced the discovery of Saint Peter's tomb.[5]
Old St. Peter's Basilica Maarten van Heemskerck – Santa Maria della Febbre, Vatican Obelisk, Saint Peter's Basilica in construction (1532)
Maarten van Heemskerck – Santa Maria della Febbre, Vatican Obelisk, Saint Peter's Basilica in construction (1532) A conjectural view of the Old St. Peter's Basilica by H. W. Brewer, 1891
A conjectural view of the Old St. Peter's Basilica by H. W. Brewer, 1891
Old St. Peter's Basilica was the fourth-century church begun by the Emperor Constantine the Great between 319 and 333 AD.[6] It was of typical basilical form, a wide nave and two aisles on each side and an apsidal end, with the addition of a transept or bema, giving the building the shape of a tau cross. It was over 103.6 metres (340 ft) long, and the entrance was preceded by a large colonnaded atrium. This church had been built over the small shrine believed to mark the burial place of St. Peter, though the tomb was "smashed" in 846 AD.[7] It contained a very large number of burials and memorials, including those of most of the popes from St. Peter to the 15th century. Like all of the earliest churches in Rome, both this church and its successor had the entrance to the east and the apse at the west end of the building.[8] Since the construction of the current basilica, the name Old St. Peter's Basilica has been used for its predecessor to distinguish the two buildings.[9]
Plan to rebuildBy the end of the 15th century, having been neglected during the period of the Avignon Papacy, the old basilica had fallen into disrepair. It appears that the first pope to consider rebuilding or at least making radical changes was Pope Nicholas V (1447–1455). He commissioned work on the old building from Leone Battista Alberti and Bernardo Rossellino and also had Rossellino design a plan for an entirely new basilica, or an extreme modification of the old. His reign was frustrated by political problems and when he died, little had been achieved.[3] He had, however, ordered the demolition of the Colosseum and by the time of his death, 2,522 cartloads of stone had been transported for use in the new building.[3][note 1] The foundations were completed for a new transept and choir to form a domed Latin cross with the preserved nave and side aisles of the old basilica. Some walls for the choir had also been built.[11]
Pope Julius II planned far more for St Peter's than Nicholas V's program of repair or modification. Julius was at that time planning his own tomb, which was to be designed and adorned with sculpture by Michelangelo and placed within St Peter's.[note 2] In 1505 Julius made a decision to demolish the ancient basilica and replace it with a monumental structure to house his enormous tomb and "aggrandize himself in the popular imagination".[12] A competition was held, and a number of the designs have survived at the Uffizi Gallery. A succession of popes and architects followed in the next 120 years, their combined efforts resulting in the present building. The scheme begun by Julius II continued through the reigns of Leo X (1513–1521), Adrian VI (1522–1523), Clement VII (1523–1534), Paul III (1534–1549), Julius III (1550–1555), Marcellus II (1555), Paul IV (1555–1559), Pius IV (1559–1565), Pius V (saint) (1565–1572), Gregory XIII (1572–1585), Sixtus V (1585–1590), Urban VII (1590), Gregory XIV (1590–1591), Innocent IX (1591), Clement VIII (1592–1605), Leo XI (1605), Paul V (1605–1621), Gregory XV (1621–1623), Urban VIII (1623–1644) and Innocent X (1644–1655).
Financing with indulgencesOne method employed to finance the building of St. Peter's Basilica was the granting of indulgences in return for contributions. A major promoter of this method of fund-raising was Albrecht, Archbishop of Mainz and Magdeburg, who had to clear debts owed to the Roman Curia by contributing to the rebuilding program. To facilitate this, he appointed the German Dominican preacher Johann Tetzel, whose salesmanship provoked a scandal.[13]
Cite error: There are <ref group=note> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=note}} template (see the help page).


































Add new comment